The kidneys are vital organs responsible for filtering waste from the blood, regulating blood pressure, and maintaining the body’s electrolyte balance. Keeping them healthy is crucial for overall well-being, and diet plays a significant role in kidney health. Certain beverages, however, can strain or damage these essential organs. Understanding which drinks to avoid can help you protect your kidneys and maintain optimal health. Here are five drinks that can be detrimental to your kidneys:
1. Sodas and Carbonated Drinks
Sodas and carbonated drinks, especially those loaded with sugar, pose a significant risk to kidney health. A 2016 study published in *Nephrology* revealed that individuals who consumed more than four sugar-sweetened sodas a week had double the risk of developing kidney disease compared to those who drank fewer. The high sugar content in these drinks can lead to obesity, diabetes, and high blood pressure—all of which are risk factors for kidney disease. Furthermore, both regular and diet sodas have been linked to the formation of kidney stones, which can further exacerbate kidney issues.
2. Processed Fruit Juice
While fruit juice is often perceived as a healthy option, processed fruit juices are often high in sugar and calories, making them potentially harmful to kidney health. Research from the Tehran Lipid and Glucose Study found that high consumption of sugar-sweetened beverages, including fruit juices, was associated with an increased incidence of chronic kidney disease. The excessive sugar intake from processed fruit juices can contribute to metabolic disorders and exacerbate kidney problems. Moderation is key, and opting for fresh fruit in its whole form is generally a healthier choice.
3. Diet Soda
Diet sodas, while free of sugar, are not without their own health risks. A study published in the *Clinical Journal of the American Society of Nephrology* in 2011 found that individuals who consumed two or more diet sodas daily were twice as likely to experience a decline in kidney function compared to those who avoided these beverages. The artificial sweeteners used in diet sodas may contribute to metabolic changes that can affect kidney health. Although diet sodas are a better alternative to regular sodas, they should still be consumed with caution.
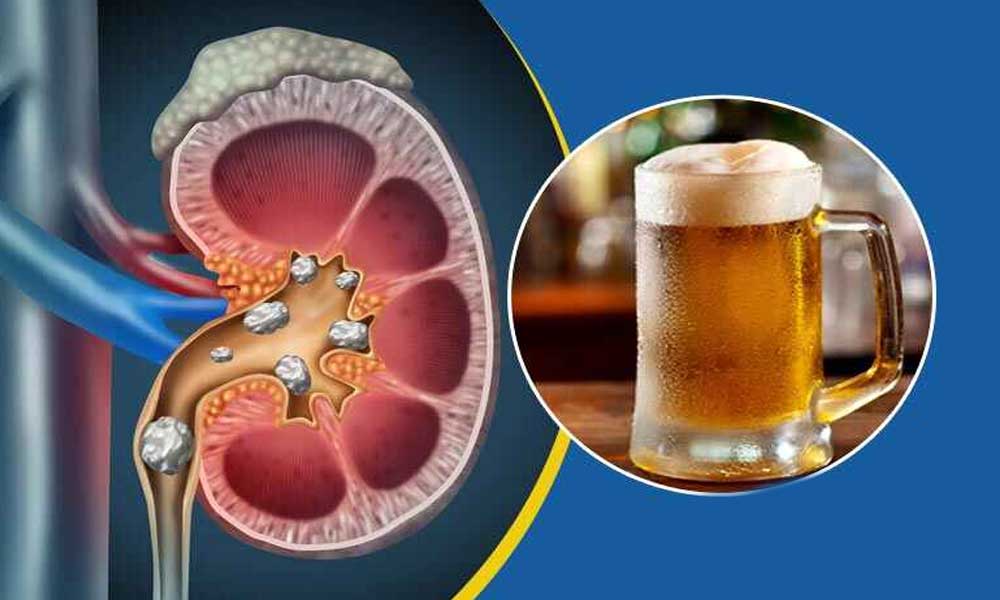
4. Alcohol
Alcohol consumption can have detrimental effects on the kidneys. Heavy drinking has been linked to increased rates of albuminuria, a condition where protein leaks into the urine and indicates kidney damage. A study published in *Nephrology Dialysis Transplantation* highlighted that regular, excessive alcohol intake significantly raises the risk of kidney disease. Alcohol can also lead to high blood pressure and dehydration, both of which negatively impact kidney function. Reducing alcohol intake can help mitigate these risks and support overall kidney health.
5. Caffeine and Energy Drinks
Caffeine, found in coffee, tea, and energy drinks (5 star, storm, run, rush, boss, etc.), can put additional strain on the kidneys. It increases blood flow and blood pressure, which can be taxing on kidney function. A 2024 study published in *Jama Network* found that caffeine’s impact on kidney health varies based on genetic factors. For individuals with certain gene mutations, coffee consumption can triple the likelihood of kidney damage. While moderate caffeine intake may not be harmful for everyone, it’s essential to be aware of its potential risks, especially for those with pre-existing kidney conditions.
Maintaining kidney health involves more than just avoiding harmful substances—it also requires a balanced diet and a healthy lifestyle. By limiting your intake of sugary sodas, processed fruit juices, diet sodas, alcohol, and caffeine, you can reduce the risk of kidney damage and support overall wellness. Additionally, staying hydrated with water, eating a nutritious diet, and undergoing regular health check-ups can further promote kidney health and prevent disease. By making informed choices about what you drink, you can play an active role in preserving the health and function of your kidneys.
 GhArticles.com Every News in Detail
GhArticles.com Every News in Detail